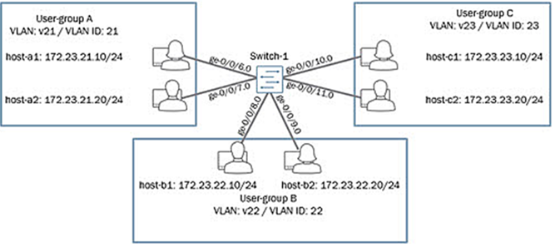
01. You are implementing the network shown in the exhibit. You must ensure that all users can communicate with each other. What are three steps that should be taken in this scenario?
(Choose three.)
a) You must define all ports as trunk ports and include all VLANs as members.
b) You must define all ports as access ports and include the appropriate VLAN as a member.
c) You must create a unique logical IRB interface for each network and assign an IP address within the appropriate network.
d) You must specify the appropriate Layer 3 IRB interface under each VLAN.
e) You must configure a single logical IRB interface with an IP address for each of the three networks.
02. You must restrict access to a printer with a persistent DHCP address of 2001:db8:0000:50::1 1:db8:0000:50::10/64 in VLAN v50 to users assigned to VLAN v50 only. Which action would satisfy this requirement?
a) Implement a firewall filter on the VLAN v50, blocking traffic to and from 2001:db8:0000:50::10.
b) Implement persistent MAC learning to ensure that 2001:db8:0000:50::10 is allocated properly.
c) Implement a firewall filter on the IRB interface for VLAN v50, blocking traffic to and from 2001:db8:0000:50::10.
d) Implement DHCP snooping on VLAN v50 to ensure that 2001:db8:0000:50::10 is allocated properly.
03. Which statement is true about the configuration shown in the exhibit?
a) The preferred next hop is 172.30.25.5.
b) 172.30.25.1 is the preferred next hop.
c) The preference for the 172.30.25.1 next hop is 7.
d) The preference for the 172.30.25.1 next hop is 5.
04. Which two statements about aggregate routes in the Junos OS are correct?
(Choose two.)
a) An aggregate route has a default next hop of an IP address.
b) An active route can contribute only to a single aggregate route.
c) Only one aggregate route can be configured for each destination prefix.
d) An aggregate route always shows as active in the routing table.
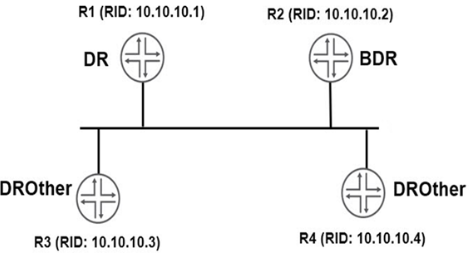
05. You have configured OSPF routing as shown in the exhibit. You notice that all interfaces have formed full adjacencies, with the exception of the interfaces connecting R3 and R4 with a status of 2Way. What is the reason for this status?
a) The two routers must both be configured as DR routers.
b) The interface-type is not configured as p2p.
c) DRother routers will not form a full adjacency with each other.
d) The two routers must be configured in different areas.
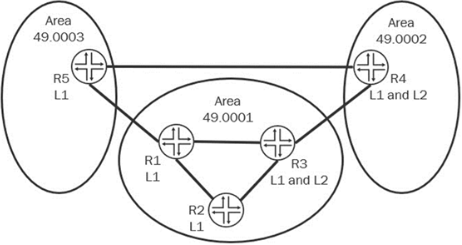
06. Referring to the exhibit, which two statements are correct?
(Choose two.)
a) R4 and R5 can form a Level 1 adjacency.
b) R3 and R4 can form a Level 2 IS-IS adjacency.
c) R1 and R5 can form a Level 1 IS-IS adjacency.
d) R2 and R3 can form a Level 1 IS-IS adjacency.
07. You are evaluating a BGP route. Unfortunately, the next hop for the route is not reachable. In this scenario, what are two ways that BGP handles this route?
(Choose two.)
a) The route is placed into the routing table as hidden routes.
b) The route is placed into the forwarding table as hidden routes.
c) The route is placed into the forwarding table as inactive routes.
d) The route is not placed into the forwarding table.
08. Which statement is true about IP-IP tunnels?
a) Intermediate devices must have a route to the tunnel destination address but do not require a route to the tunnel source address.
b) Intermediate devices must have a route to the destination address of the traffic being tunneled.
c) Intermediate devices must have a route to both the tunnel source address and the tunnel destination address.
d) Intermediate devices must have a route to the tunnel source address but do not require a route to the tunnel destination address.
09. Which two statements describe NSR?
(Choose two.)
a) NSR requires GRES to function properly.
b) NSR rapidly detects link failures.
c) NSR provides routing loop protection.
d) NSR provides high availability with multiple Routing Engines.
10. Which two statements about a unified ISSU are correct?
(Choose two.)
a) It requires that graceful Routing Engine switchover be enabled.
b) It is only supported on platforms with redundant control planes.
c) It is only supported on platforms with redundant power supplies.
d) It requires that Bidirectional Forwarding Detection be disabled.
 Before you write the Juniper JNCIS Routing and Switching (JN0-351) certification exam, you may have certain doubts in your mind regarding the pattern of the test, the types of questions asked in it, the difficulty level of the questions and time required to complete the questions. These Juniper Networks Certified Specialist Enterprise Routing and Switching (JNCIS-ENT) sample questions and demo exam help you in removing these doubts and prepare you to take the test.
Before you write the Juniper JNCIS Routing and Switching (JN0-351) certification exam, you may have certain doubts in your mind regarding the pattern of the test, the types of questions asked in it, the difficulty level of the questions and time required to complete the questions. These Juniper Networks Certified Specialist Enterprise Routing and Switching (JNCIS-ENT) sample questions and demo exam help you in removing these doubts and prepare you to take the test.